Causes Of Sinusoidal Pattern
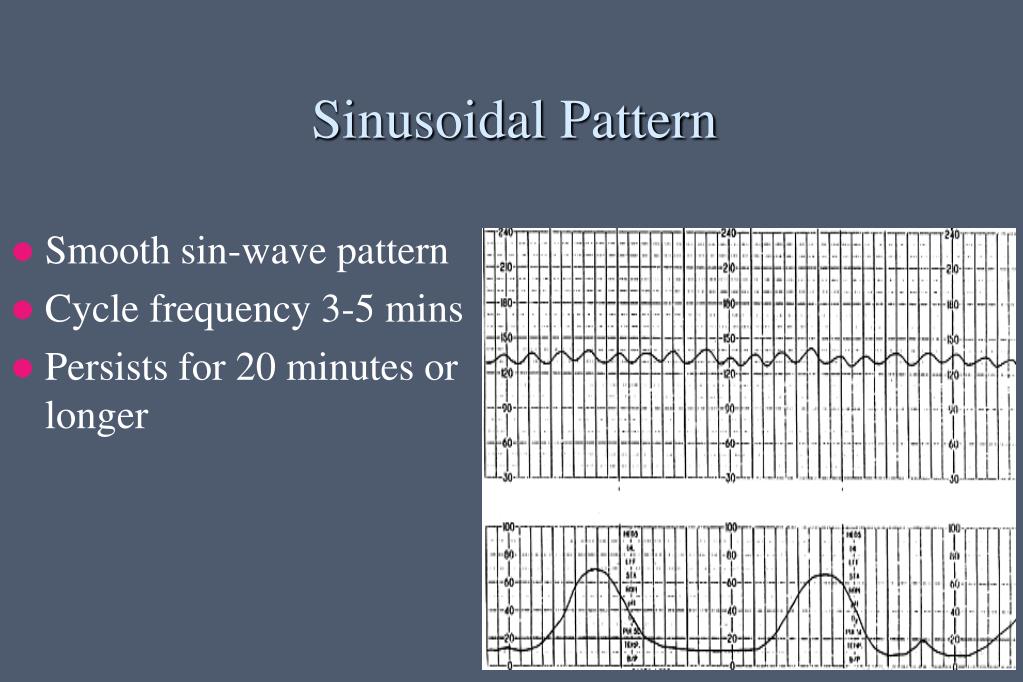
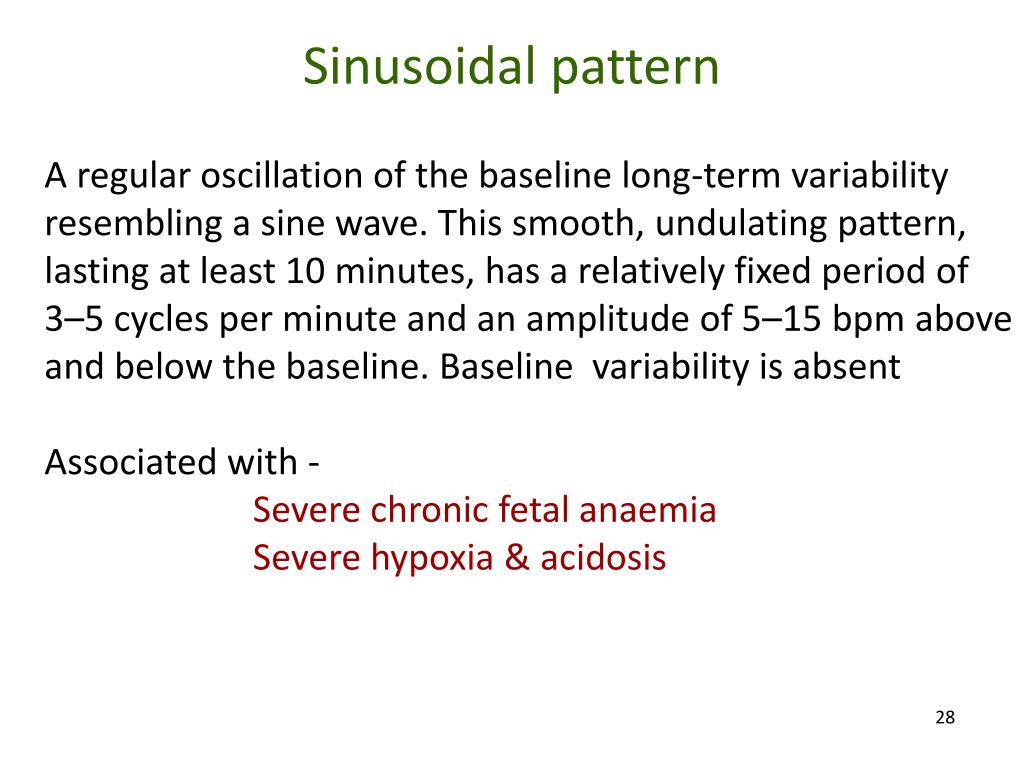
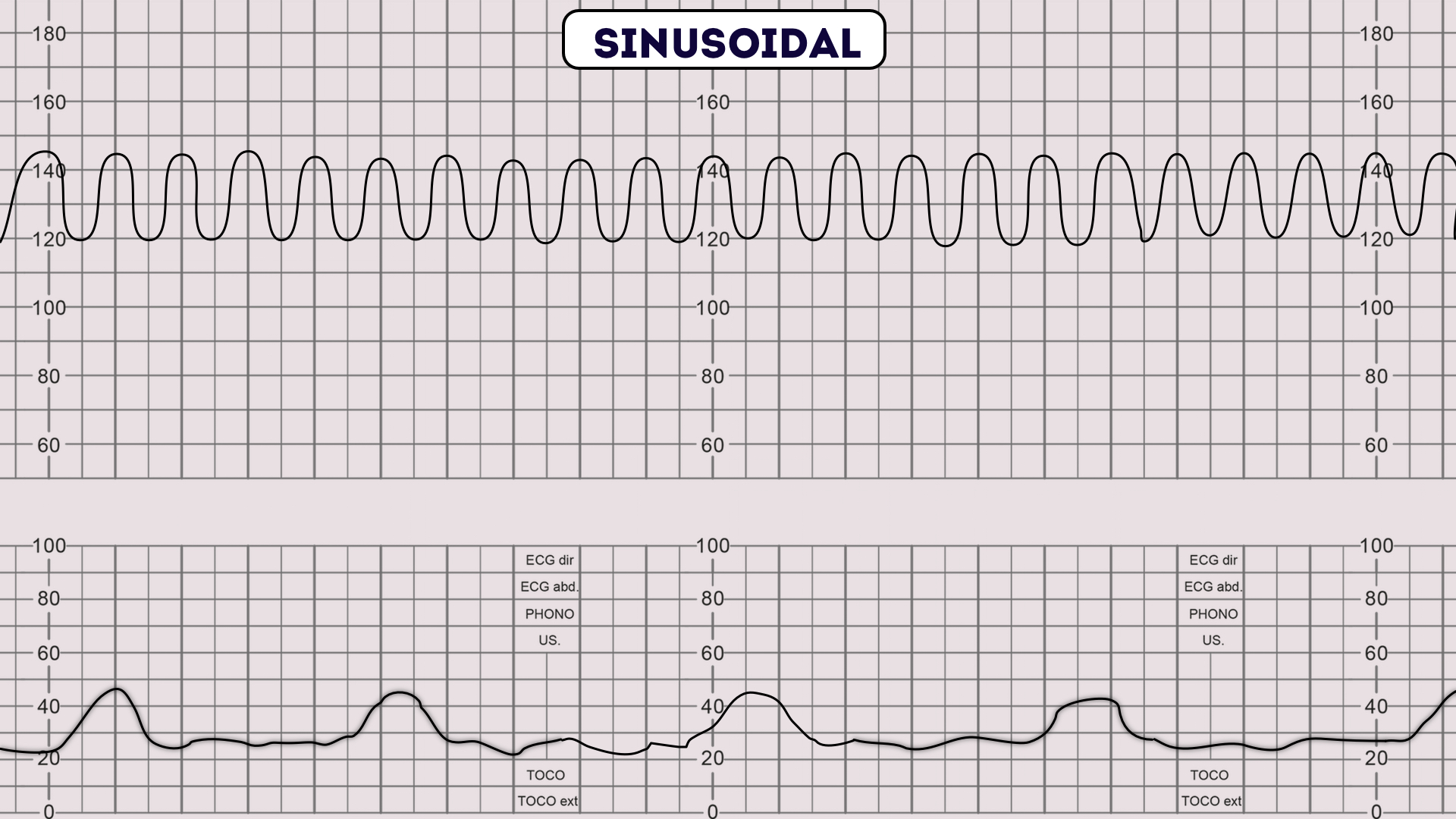
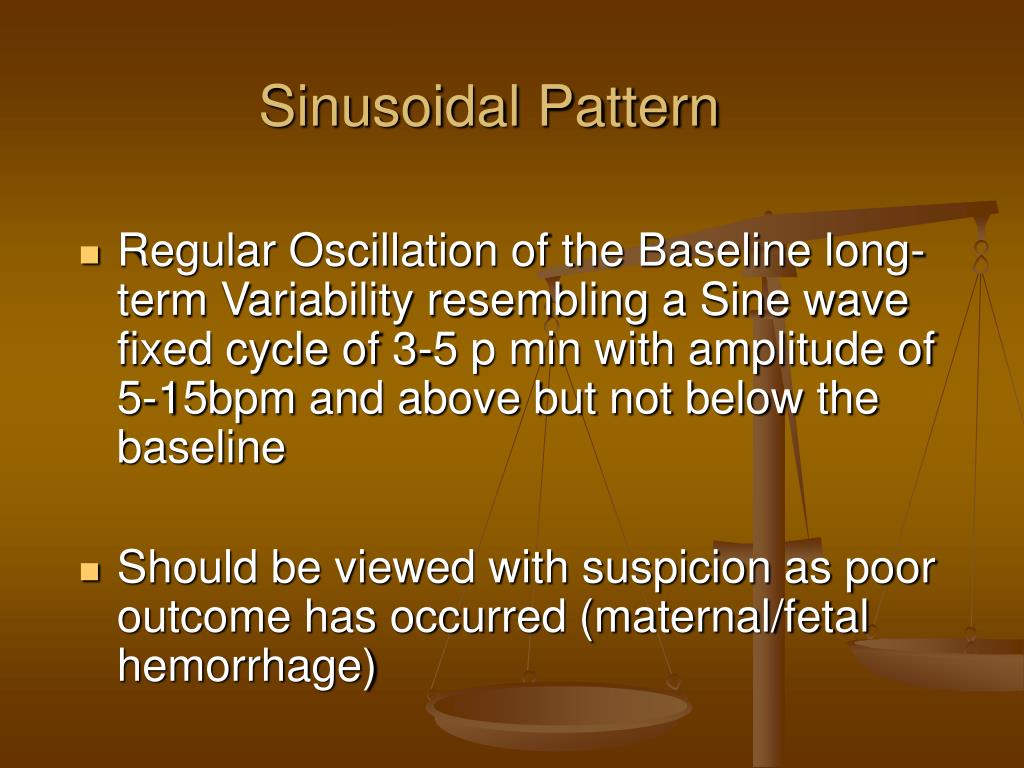
Causes Of Sinusoidal Pattern - It is typically reflective of severe anaemia, with No beat to beat variability; In 1972, manseau et al. Web a sinusoidal pattern is an oscillating pattern which is typically smooth and regular. (2) effects of drugs, particularly narcotics; Web sinusoidal fetal heart rate pattern (fhr) is regarded by most authors as signifying a compromised fetus. 136587, 1980.) the sinusoidal fetal heart rate (shr) isconsidered indicative of severe fetal jeopardy by most authors. It has also been described in association with chorioamnionitis, diabetes, and preeclampsia [11] , [51]. Four patients who demonstrated sinusoidal fhr patterns are reported, and the factors associated with these patterns and their effect on fetal outcome are discussed. Shr pattern has been reported with the following fetal conditions: (1) severe fetal anemia of several etiologies; To address the clinical significance of sinusoidal heart rate (shr) pattern and review its occurrence, define its characteristics, and explain its physiopathology. Based on this analysis, stricter criteria are presented whereby the true sinusoidal pattern can be diagnosed and distinguished from the pseudosinusoidal. A sinusoidal pattern usually indicates one or more of the following: Strict adherence to definition is important, as pseudosinusoidal patterns do not have the same grave prognostic significance. Web a sinusoidal ctg pattern has the following characteristics: (2) effects of drugs, particularly narcotics; It has also been described in association with chorioamnionitis, diabetes, and preeclampsia [11] , [51]. And (7) sucking and rhythmic movements. Massive fetomaternal hemorrhage occurs in one in 1000 deliveries and has been associated with decreased fetal movements and a sinusoidal fetal heart rate (fhr) pattern. It is typically reflective of severe anaemia, with In most cases, this is secondary to fetal anemia of different causes, usually rh isoimmunization, more rarely to fetomaternal transfusion, bleeding vasa previa, placental chorioangioma, or trauma. Web fetal conditions associated with shr pattern: Web sinusoidal pattern or absent variability with recurrent late decelerations, recurrent variable decelerations, or bradycardia. 136587, 1980.) the. The sinusoidal pattern is associated with severe fetal anaemia, although the pathophysiologic mechanism has not been definitively proven. The sinusoidal fetal heart rate pattern is significantly associated with severe fetal anaemia when seen in the antenatal period. Web the primary cause of sinusoidal patterns is fetal anemia, currently attributed to fetomaternal transfusion (fmt) [10]. Paired contractions, which are contractions that. Four patients who demonstrated sinusoidal fhr patterns are reported, and the factors associated with these patterns and their effect on fetal outcome are discussed. Based on this analysis, stricter criteria are presented whereby the true sinusoidal pattern can be diagnosed and distinguished from the pseudosinusoidal. It is typically reflective of severe anaemia, with Web a sinusoidal ctg pattern has the. And (7) sucking and rhythmic movements. This fhr pattern was called ‘sinusoidal’ because of. (2) effects of drugs, particularly narcotics; Shr pattern has been reported with the following fetal conditions: Web a specific definition of shr was made in order to elucidate its clinical significance. Web the etiology of sinusoidal fetal heart rate (fhr) patterns is diverse and consequently they have been associated with poor as well as normal fetal outcome. Based on this analysis, stricter criteria are presented whereby the true sinusoidal pattern can be diagnosed and distinguished from the pseudosinusoidal. Web a sinusoidal pattern is an oscillating pattern which is typically smooth and. Web fetal conditions associated with shr pattern: The sinusoidal fetal heart rate pattern is significantly associated with severe fetal anaemia when seen in the antenatal period. And (7) sucking and rhythmic movements. Paired contractions, which are contractions that are coupled together, one after the other, then a prolonged gap in uterine activity occurs before the next set of paired contractions.. Strict adherence to definition is important, as pseudosinusoidal patterns do not have the same grave prognostic significance. (1) severe fetal anemia of several etiologies; 0.14 and 1.4 percent, respectively; Web category iii tracings have the highest risks of umbilical artery ph <7.0 and hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (31 and 19 percent, respectively), while the risks of both are lower and not. Web the etiology of sinusoidal fetal heart rate (fhr) patterns is diverse and consequently they have been associated with poor as well as normal fetal outcome. Web a sinusoidal pattern is an oscillating pattern which is typically smooth and regular. 136587, 1980.) the sinusoidal fetal heart rate (shr) isconsidered indicative of severe fetal jeopardy by most authors. Web sinusoidal pattern. The sinusoidal fetal heart rate pattern is significantly associated with severe fetal anaemia when seen in the antenatal period. Depending on the clinical situation, efforts to expeditiously resolve the underlying cause of the abnormal fetal heart rate pattern should be made. (2) effects of drugs, particularly narcotics; No beat to beat variability; Based on this analysis, stricter criteria are presented. Reports on fluctuating fetal heart rate (fhr) patterns, which have been called sinusoidal fhr patterns in the literature, have been critically reviewed. Four patients who demonstrated sinusoidal fhr patterns are reported, and the factors associated with these patterns and their effect on fetal outcome are discussed. Based on this analysis, stricter criteria are presented whereby the true sinusoidal pattern can. And (7) sucking and rhythmic movements. Web sinusoidal pattern is exceedingly rare and thus intervention has not been studied in a systematic way. It is typically reflective of severe anaemia, with (1) severe fetal anemia of several etiologies; In most cases, this is secondary to fetal anemia of different causes, usually rh isoimmunization, more rarely to fetomaternal transfusion, bleeding vasa previa, placental chorioangioma, or trauma. Baseline variability is absent and there are no accelerations. (1) severe fetal anemia of several etiologies; Massive fetomaternal hemorrhage occurs in one in 1000 deliveries and has been associated with decreased fetal movements and a sinusoidal fetal heart rate (fhr) pattern. Based on this analysis, stricter criteria are presented whereby the true sinusoidal pattern can be diagnosed and distinguished from the pseudosinusoidal. Shr pattern has been reported with the following fetal conditions: Shr pattern has been reported with the following fetal conditions: Web the most common cause of a tachysystolic, polysystolic or hypertonic contraction pattern is oxytocin or prostaglandins. This fhr pattern was called ‘sinusoidal’ because of. Depending on the clinical situation, efforts to expeditiously resolve the underlying cause of the abnormal fetal heart rate pattern should be made. The sinusoidal pattern is associated with severe fetal anaemia, although the pathophysiologic mechanism has not been definitively proven. (2) effects of drugs, particularly narcotics;PPT Electronic Fetal Monitoring PowerPoint Presentation, free
[PDF] Title Sinusoidal heart rate pattern Reappraisal of its
PPT Basic Fetal Monitoring Review PowerPoint Presentation ID6960616
Sinusoidal fetal heart rate
(PDF) Sinusoidal fetal heart rate pattern Its definition and clinical
PPT ELECTRONIC FETAL MONITORING (EFM) / CARDIOTOCOGRAPHY(CTG
PPT Fetal Heart Rate Interpretation PowerPoint Presentation, free
MBBS Medicine (Humanity First) Assessment of Fetal Wellbeing
PPT Cardiotocography ( CTG ) Electronic Fetal Monitoring PowerPoint
How to Read a CTG CTG Interpretation Geeky Medics
Shr Pattern Has Been Reported With The Following Fetal Conditions:
Web The Sinusoidal Fetal Heart Rate Pattern Has Been Reported To Be An Indication Of Fetal Compromise.
No Beat To Beat Variability;
(2) Effects Of Drugs, Particularly Narcotics;
Related Post:
![[PDF] Title Sinusoidal heart rate pattern Reappraisal of its](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/6d5e7a69191cbbf8b191de0cda503d5693a11acc/6-Figure2-1.png)